Stem Cell Therapy for Muscular Dystrophy in Turkey
Stem Cell
If you’re seeking for the limitless potential of Stem Cell Therapy for Muscular Dystrophy, you’ve come to the correct place!
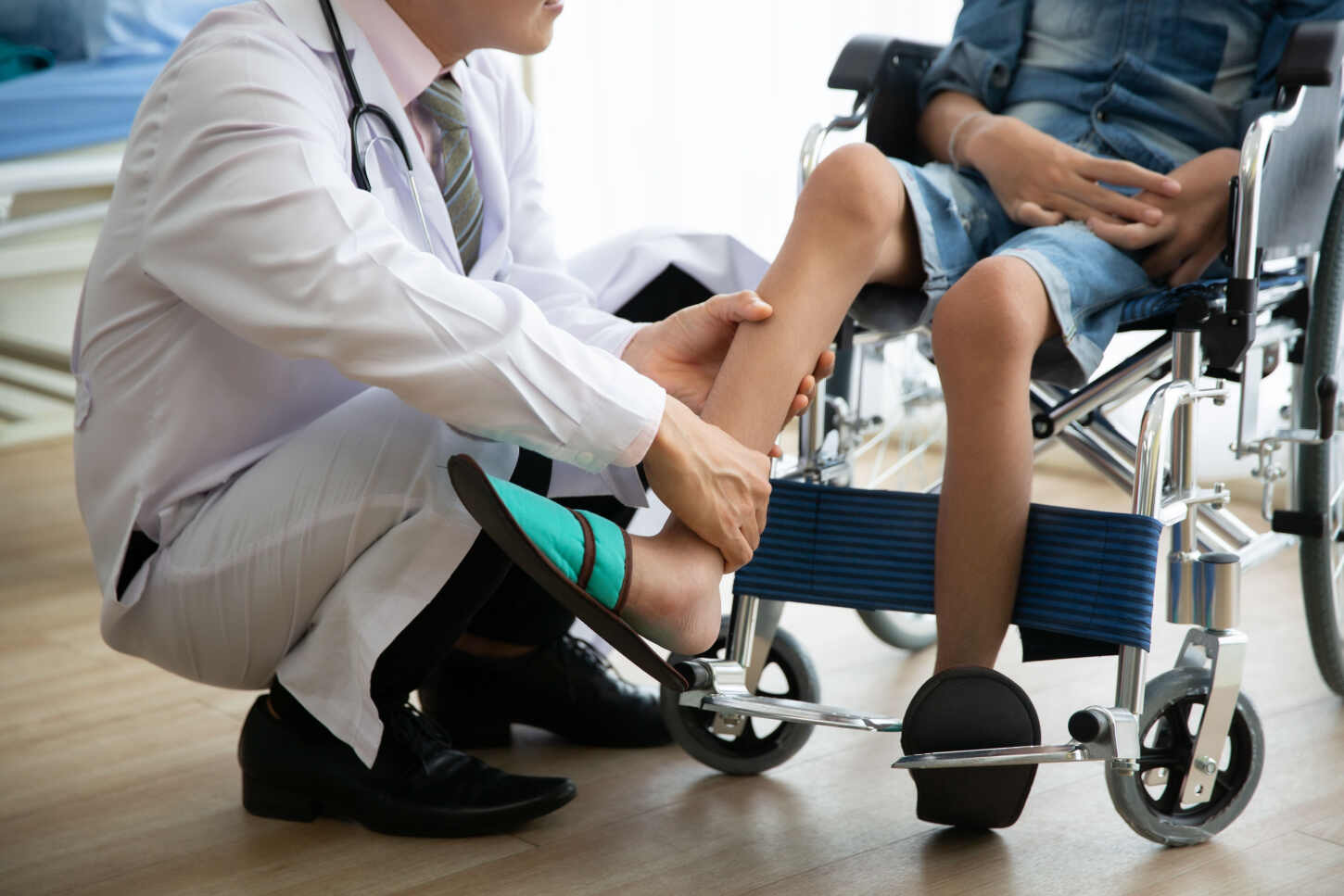
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of inherited muscle diseases that steadily weaken muscles, causing increasing disability. It gets worse over time, typically starting in specific muscle groups and spreading. Some types can even threaten life by affecting the heart or breathing muscles. While there’s no cure, treatments can manage many symptoms.
Who is more likely to get muscular dystrophy?
Anyone can get muscular dystrophy, but some people are more at risk:
- Family history: Having family with MD increases your chance of getting it.
- Gene changes: Faulty genes can cause MD, sometimes appearing even when parents don’t have it.
- Inheritance: MD can be passed down in three ways:
- One faulty gene from one parent (autosomal dominant)
- Two faulty genes from both parents (autosomal recessive)
- Faulty gene from mother to son (X-linked recessive)
Remember, even if you’re at risk, it doesn’t mean you’ll definitely get MD.
There are many different types of MD. Some of the most common types include:
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common type of MD. It is a severe form of the disease that usually affects boys. People with DMD typically lose the ability to walk by the age of 12, and they rarely live past the age of 30.
- Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) is similar to DMD, but it is a milder form of the disease. People with BMD typically retain the ability to walk, and they may live into adulthood.
- Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is a slowly progressive form of MD that affects the muscles of the face, shoulders, and upper arms. People with FSHD may experience difficulty with speech, swallowing, and shoulder movement.
- Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) is a group of diseases that affect the muscles of the arms and legs. LGMD can be mild or severe, and the age of onset varies depending on the type of LGMD.
The cause of MD is a genetic mutation. These mutations can be inherited from parents or they can occur spontaneously.
There is no cure for MD. However, there are treatments that can help to improve symptoms and quality of life. These treatments include physical therapy, medication, and surgery.
Stem cells are special cells that can multiply and become different types of cells in your body. They’re like tiny repair crews that can potentially fix damaged tissues. Researchers are still studying how to use stem cell therapy for muscular dystrophy. Early studies have shown that stem cell therapy can improve muscle function and reduce the progression of the disease.
For treating muscular dystrophy, stem cell therapy can be used for replacing damaged muscle cells, producing growth factors that help to repair muscles and creating new muscle tissue.
Stem cell therapy for muscular dystrophy is a promising new treatment. With further research, this treatment could provide a new way to improve the lives of people with this disease.
We understand the challenges caused by stroke, and are here to support you on every step of your recovery journey. Don’t hesitate to reach out for details about treatment options, potential outcomes, and any other questions you may have about stem cell therapy for muscular dystrophy.
Contact us today and let us help navigate your path to better health.
All you need to know about stem cell therapy is right here, contact us now!
FAQ
What is muscular dystrophy?
It’s a group of inherited muscle diseases that gradually weaken muscle tissue, making movement harder.
How common is muscular dystrophy?
While anyone can get it, some people are more at risk due to family history or genetic changes.
Who is more likely to get MD?
Having family with MD, specific gene changes, and inheriting the faulty gene in certain ways increase the risk.
Contact us now in case you have any questions!
Types of Treatments
Powered by ISSCA, REGEN, and MedClinics - connecting a global network of pioneers to shape the future of regenerative medicine.
Cell-Free Regeneration | The Intelligent Power of Exosomes
Heal from Within | The Power of Stem Cells
Request Form
Get your free consultation
- Need guidance and reassurance?
- Talk to a real person from MedClinics!
- Let's find the perfect doctor together.